If you are looking for a single product for your hair, skincare, and body, you should consider Camellia oil. It is an easy-to-use, nutrient-rich moisturizer that also acts as an emollient to keep your skin and hair soft and supple.
Camellia Oil Benefits for Skin and Hair: An Overview
Japanese Camellia oil is a rich source of Oleic, Linoleic, and Palmitic fatty acids, plus numerous anti-aging polyphenol antioxidants. It is non-greasy and an excellent all-around moisturizer/emollient for the skin and hair.
 Approximately 82% of its fatty acids are composed of Oleic fatty acid (Omega-9), a remarkable transdermal carrier and very effective in enhancing skin and hair's ability to retain moisture.
Approximately 82% of its fatty acids are composed of Oleic fatty acid (Omega-9), a remarkable transdermal carrier and very effective in enhancing skin and hair's ability to retain moisture.
Camellia oil absorbs very quickly. It permeates deep into lower layers of skin, promoting cell growth, and giving skin support and flexibility.
Japanese Camellia oil is best when cold-pressed from seeds of yabu-tsubaki, the wild variety of Camellia japonica flower (yabu means wild in Japanese, tsubaki means camellia).
Benefit List: A Quick Look
- All-in-One Solution: Ideal for those seeking a single, easy-to-use product that nourishes, moisturizes, and softens skin and hair.
- Rich in Nutrients: Packed with essential fatty acids and antioxidants for holistic nourishment.
- Moisturizing Excellence: Offers superior hydration without a greasy feel.
- Deep Absorption: Quickly penetrates skin and hair for immediate benefits.
- Enhanced Elasticity: Promotes skin flexibility and resilience.
- Pure and Natural: Cold-pressed from wild Camellia japonica seeds for purity and potency.
Table of Contents
Camellia Oil for Hair Care
- How to Use Camellia Oil for Hair Care ↗
- How to Use Camellia Oil as Deep Treatment Pack ↗
- How to Use Camellia Oil with Seaweed Hair Cleanser ↗
- Applying Camellia Oil With Tsuge Wood Comb ↗
Camellia Oil for Skincare and Facial Use
- How to Use Camellia Oil for Skincare ↗
- Use in Combination with Rice Bran Oil ↗
- Vitamin E and Sunblock Properties ↗
Camellia Oil for Body Care
Camellia Japonica and Other Varieties
Camellia Oil for Hair Care
With its golden color and creamy texture, Japanese Camellia oil has been responsible for the classic, legendary beauty of Japanese hair for centuries.
In Japan, Camellia oil is commonly used as a leave-in, best when applied to damp hair such as after showering. How much to use is a matter of personal preference. A little goes a long way, though you can use more if you like. Geishas and maikos apply a lot for the distinct Japanese traditional glossy hair look they prefer.
If you have difficult, unmanageable hair, you can apply Camellia oil before washing to untangle and make it more manageable.
Camellia Oil's Extensive Benefits for Hair
- Enhances Softness: Softens hair and makes it more manageable.
- Natural Sheen: Restores and amplifies hair's natural glow.
- Moisture Lock: Helps hair retain essential moisture.
- Pollution Barrier: Forms a protective shield against environmental pollutants.
- Damage Repair: Helps mend breakage and split ends for stronger hair.
- Scalp Soothing: Alleviates dryness and itchiness.
- Dandruff Prevention: Keeps dandruff at bay for a clean, healthy scalp.
- Color & Perm Recovery: Treats and revitalizes hair damaged by perms and coloring.
How to Use Camellia Oil for Hair Care
For the Japanese, the most common use of Camellia oil is to apply it to hair after washing.
Regular Application
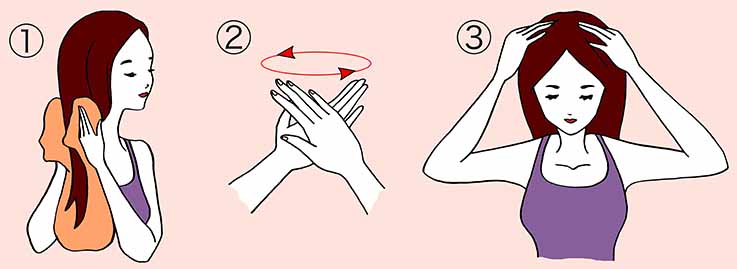
For optimal hair health and shine, follow these simple steps after washing:
- Towel Dry: Start with towel-dried hair.
- Spread the Oil: Place a few drops of Camellia oil in your palms and spread well.
- Apply: Begin at the top and gently massage the oil into your hair and scalp using your fingertips.
Note: Give extra attention to the hair ends, as they are often drier and more prone to breakage and damage.
Feel free to apply the oil to dry hair on non-wash days for continuous nourishment and shine.
Deep Treatment Pack
As a deep hair treatment pack, Camellia oil helps restore brilliance to dull and damaged hair.
- Prep Hair: Apply a few drops of Camellia oil to your hair before washing.
- Cover Hair: Place a shower cap over your hair, then wrap it with a towel.
- Wait: Allow the oil to penetrate for about 30 minutes.
- Wash: Shampoo and rinse your hair as usual.
Use With Seaweed Hair Cleanser
You can apply Camellia oil as moisturizer and conditioner after washing hair with seaweed hair cleanser.
 Japanese seaweed hair cleanser is fine-powdered seaweed. When you mix with water, you get a gel-like mixture.
Japanese seaweed hair cleanser is fine-powdered seaweed. When you mix with water, you get a gel-like mixture.
You can apply it in different ways. The traditional Japanese way is to use it by itself. You can also use it as a deep treatment pack, or mix it with your shampoo.
The Japanese Traditional Way
- Prepare the Mixture: Mix 1/2 tsp of seaweed powder with 3 Tbsp of hot water.
- Cool Down: Allow the mixture to cool to a comfortable temperature.
- Apply: Apply the cooled mixture evenly to your hair and scalp.
- Rinse: Rinse your hair thoroughly to remove the seaweed mixture.
- Towel Dry: Gently towel dry your hair to remove excess water.
- Apply Camellia Oil: Finish by applying a few drops of Camellia oil for added moisture and shine.
Apply Camellia Oil With a Tsuge Wood Comb
Applying Camellia oil to hair by hand is OK. Going over it with a wood comb results in a much better and more even coverage. Let hair dry before combing, as you should never comb your hair when it is wet.

Japanese traditional combs are made from Tsuge (Boxwood) — one of the densest, hardest types of wood. They are polished, one tooth at a time, to a very smooth finish.
The wood teeth have microscopic pores which pick up and re-distribute Camellia oil in a thin, even layers throughout hair. This promotes natural shine and gloss while using less Camellia oil.
Tsuge combs do not snag since their teeth are seamless. They are also anti-static as not to cause frizz when combing.
Camellia Oil for Skincare and Facial Use
Camellia oil is a fast-absorbing moisturizer which penetrates deep into the skin and restores bounce and elasticity. It has a silky, creamy texture and is non-comedogenic (does not block skin pores).
Camellia oil is a transdermal carrier of collagen and elastin. It repairs damage caused by dryness, sun exposure, and aging.
How to Use Camellia Oil for Skincare
- Pump a small amount into the palm of your hand.
- Rub your palms together to spread the oil into a thin layer.
- Pat the oil over your face and neck. Do not rub hard.
- Spread the oil in small circular motions till absorbed.
To diminish small wrinkles and blemishes, add a small drop to your fingertips and apply directly on the areas you need.
Using Camellia and Rice Bran Oils in Combination
Rice bran oil is rich in Tocotrienols, a potent form of vitamin E, and Gamma-oryzanol, an antioxidant known for its anti-aging properties. Combining this oil with Camellia oil can offer a range of skincare benefits due to the distinct properties of each.
While it's okay to mix Camellia and rice bran oils, it is best to apply them separately. Both get absorbed into the skin rapidly; you can apply one in a few minutes after applying the other.
Vitamin E and Sunblock Properties
Vitamin E
Although there are numerous claims that Camellia oil is rich in vitamin E, such claims are simplistic and can be misleading.
Vitamin E comes in many forms. Notable ones are Tocotrienols, the so-called "super vitamin E," and the more common Tocopherols. Camellia oil contains moderate levels of the Tocopherols (about 60 mg/1000 g).
Note: For a moisturizer with high Tocotrienols content, rice bran oil at 600-800 mg /1000 g is an excellent choice.
Sunblock Properties
The all too frequent claims of Camellia oil having significant sunblock properties are exaggerated.
All vegetable-based moisturizer oils, including Camellia oil, have an SPF of about 3-5. While Camellia oil is an excellent choice in skincare for its moisturizing and nourishing benefits, it should not be solely relied upon for sun protection.
Camellia Oil for Body Care
Camellia oil is a nutrient-rich skin moisturizer and softener.It is an excellent all-body moisturizer, and also does a great job to soften rough elbows, legs, knees, and heels, plus helps heal minor scars and stretch marks.
How to Use Camellia Oil for Body Care
- Apply a small amount to damp skin after showering or taking a bath.
- Apply gently and thoroughly till completely absorbed.
- Use in the morning and at night, or as often as needed.
Nail and Cuticles Care
Camellia oil softens dry or brittle nails and rough cuticles. It also helps alleviate discomfort from dry skin under and keeps nails nourished, smooth and shiny.
- Wash hands thoroughly with lukewarm water.
- Add one or two drops to a cotton pad.
- Wipe nails and cuticles with the pad.
- Massage in gently.
After a few days, you will notice that your nails and cuticles are softer and smoother and look healthier.
Camellia Japonica vs. Other Varieties
The Camellia family includes a vast number of species. Besides the all-important Camellia japonica (Tsubaki), the Camellia family includes many other plants such as Camellia sinensis (the common tea plant) and Camellia oleifera (notable for its edible properties).
Though they all are commonly referred to as "Camellia," they have significant differences and should not be confused.
 Camellia Japonica |
 Camellia Sinensis |
 Camellia Oleifera |
Camellia Japonica
Camellia japonica is the authentic Japanese Camellia native to southern Japan. It is called tsubaki in Japanese, shortened from tsuya-ba-ki, meaning "shiny leaf tree." The tsubaki tree blooms in winter and early spring, when its much-admired flower is a common sight in cities and the countryside.
The classic Japanese Camellia japonica variety is the traditional red Camellia named yabu-tsubaki (wild Camellia). The Camellia oil from its seeds is called tsubaki-abura.
It is easy to recognize yabu-tsubakis. They are dark pink to red, with five petals connected at the bottom in a cup shape. The upper sides of the leaves have a distinct waxy coating that sparkles in the light.
Camellia Sinensis
Camellia sinensis is called the tea plant. Its leaves are used to produce all teas we drink, including green, black, pu-erh, and oolong teas.
Camellia sinensis has two major varieties: var. asamica and var. sinensis. The oil from the seeds of Camellia sinensis is called Tea Oil Camellia.
Camellia Oleifera
Camellia oleifera is mainly used for making edible cooking oil. It is widely grown in China and is similar to olive oil in composition. The oil from its seeds is commonly known as Oil-seed Camellia or Tea-seed Oil.
Collection of Matured Seeds
 The traditional Japanese method for collecting Camellia seeds is to gather the seed pods by hand after fully maturing in autumn.
The traditional Japanese method for collecting Camellia seeds is to gather the seed pods by hand after fully maturing in autumn.
The work is an intensely manual process, and can only be done on a small scale.
The seed pods are sun-dried, which causes their woody shells to crack open naturally, exposing the seeds inside.
The oil pressed from the seeds has an intense golden color and a creamy, velvety texture.
Camellia Oil Extraction Methods
Cold Pressing
 Camellia oil retains its maximum benefits when extracted by cold pressing, without any refining.
Camellia oil retains its maximum benefits when extracted by cold pressing, without any refining.
Cold pressing is a labor-intensive process that preserves camellia oil's natural character and nutritional content.
Our Aya camellia oil is cold-pressed using the traditional tamajime method, a low-temperature manual pressing technique long used in Japan.
Cold pressing yields only about 20-30% of the seed's available oil, which accounts for the relatively higher cost and lower availability of quality Camellia oils.
Heat Extraction
Heat extraction is the application of high heat in conjunction with mechanical pressure to extract more oil from the seeds.
Heat extraction increases the yield to 60-70% of the seed's available oil, which reduces production costs. However, heat changes the composition of the oil and degrades its antioxidant and nutritional properties.
Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction is a standard industrial method for extracting oil from seeds, and most camellia oils available in the market are produced this way. Solvent extraction increases the yield to up to 98% of the seed's available oil and lowers production costs.
In this process, camellia seeds are subjected to high heat (around 150° C) and strong solvents like ethanol or hexane to extract the oil fully.
Although the oil undergoes distillation to remove the solvents, trace amounts of these potentially harmful chemicals can remain, raising concerns about purity and safety.
Cold-Pressed vs. Cold-Filtered
It's essential to distinguish between "cold-pressed" and "cold-filtered" when purchasing oils, as they indicate different production methods and quality levels.
In the United States and Australia, the term "cold-filtered" is often used in marketing. It might suggest a similar quality as cold-pressed, but it's not the same. Oils labeled "cold-filtered" might have been processed with heat and solvents to extract the oil. After extraction, the oil is cooled and filtered to improve its clarity and appearance.
In the European Union, Japan, and several other countries, "cold-pressed" is strictly regulated. Oils labeled as such are genuinely extracted without heat, preserving the oil's natural properties and nutritional value.
While "cold-pressed" assures that the oil is extracted at low temperatures without chemical solvents, "cold-filtered" does not offer the same guarantee.
Why Unrefined Oils are Better
Unrefined oils, including Camellia oil, are celebrated for their pure, unaltered state. These oils are extracted and produced without excessive heat or chemical solvents, ensuring their natural, beneficial compounds remain intact.
Rich in Nutrients
Unrefined Camellia oil is teeming with nutrients. It boasts a high concentration of oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid that nourishes and moisturizes the skin and hair. The oil is also rich in antioxidants, which protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Gentle Extraction Process
The extraction process for unrefined oils is gentle and non-invasive. It doesn’t involve high temperatures or harsh chemicals, which can degrade the oil’s quality and diminish its nutritional content. As a result, unrefined oils retain their natural aroma, color, and nutritional value.
The Downside of Refined Oils
In contrast, refined oils are often stripped of their natural nutrients during extraction due to exposure to high heat and chemical solvents, resulting in an oil that lacks the nutritional richness of its unrefined counterpart.