Understanding Herbal Teas and Their Consumption
Herbal teas are flavorful infusions crafted from various parts of plants, including leaves, roots, stems, twigs, barks, and occasionally fruits. Due to their non-concentrated nature, they're typically deemed safe for consumption.
Japan boasts a rich tradition of savoring herbal teas, not just for their delightful taste but also for their myriad benefits. While we draw our knowledge from trusted sources, traditional Japanese practices, and cultural insights, please remember that this information doesn't replace professional medical advice.
In the sections below, we'll introduce you to 12 distinct Japanese herbal teas, providing a quick lookup for their top benefits, followed by detailed descriptions. We have also provided links for more in-depth reading and preparation instructions for each tea.
Japanese Herbal Teas at a Glance: Top Benefits
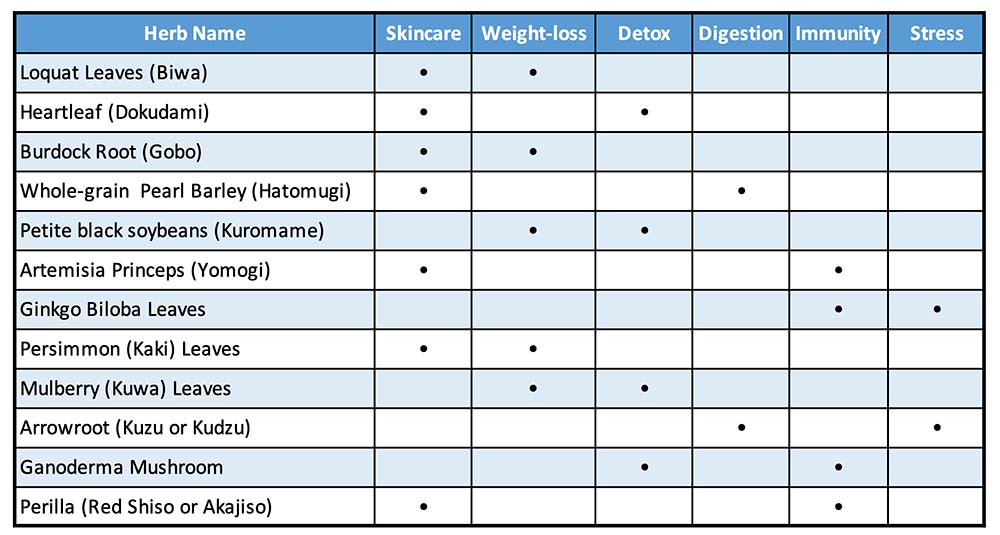
12 Japanese Herbal Teas: Detailed Profiles
Japanese Loquat Leaves (Biwa)
This traditional Japanese herb has a mild, earthy taste, a subtle hint of sweetness, and beneficial effects in treating numerous diseases. It contains potent antioxidants and polyphenols that can boost general health, improve respiratory ailments, lower blood lipid and sugar levels, and alleviate inflammatory skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis (eczema), among other benefits.
Japanese Heartleaf (Dokudami)
This traditional Japanese herb helps rid the body of harmful toxins and fight infectious ailments. The Japanese consider dokudami a cure-all plant and affectionately call it jūyaku, meaning "ten medicines." It detoxifies the body, combats infections, enhances stamina, and boosts cognitive health, and there are numerous scientific studies on its potent antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-fungal properties.
Japanese Burdock Root (Gobo)
Japanese Burdock Root, known as Gobo, is used to make a traditional tea celebrated for its myriad health benefits. With a pleasant, roasty, bittersweet, and earthy flavor, it's a favorite for those looking to improve skin health and gastrointestinal well-being. Its benefits for the skin include combating the growth of acne-causing bacteria, tightening pores, refining the skin's texture, and increasing circulation. Beyond skincare, Gobo is known to help stimulate the digestive tract, relieving constipation, cramps, and bloating, making it a holistic choice for overall health.
Whole-grain Japanese Pearl Barley (Hatomugi)
Hatomugi, known as pearl barley or adlay millet, is hailed as a skin miracle grain in Japan. Frequently recommended by Japanese dermatologists, it enhances skin complexion, softens, reduces blemishes, and combats sun damage. Rich in vitamins B1, B2, and B3, it contains antioxidants like ferulic acid that protect against UV damage and lignans that reduce inflammation, thereby slowing melanin production and lightening skin tone.
Petite Variety Japanese Black Soybeans (Kuromame)
The petite Japanese black soybeans, known as Kuromame, stand out as a flavorful super-food packed with nutritional benefits. With high protein and low carb content, they offer twice the antioxidants of regular black soybeans and five times more than yellow soybeans. Key benefits include promoting stronger bone density, supporting heart health by lowering blood pressure and reducing LDL cholesterol, boosting immunity, as well as being a low-carb option beneficial for weight management.
Artemisia Princeps (Yomogi) Leaves
Japanese Artemisia Princeps, commonly known as Yomogi, is known for its greeny-lemony undertones and rejuvenating aroma. Historically, the Japanese have revered Yomogi for promoting beauty and improving gynecological health. The wild-harvested Yomogi leaves used in the tea are packed with antioxidants that offer anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, and cancer-combating benefits. Its benefits include soothing inflammatory skin issues, improving skin tone, reducing age spots, and alleviating menstrual discomforts. Additionally, it aids in hormonal balance, boosts reproductive health, and offers protection against certain cancers.
Japanese Ginkgo Biloba Leaves
Ginkgo Biloba is commonly used for enhancing memory and improving circulatory disorders. Its antioxidants help protect the body from the damaging effects of free radicals. They also contain a unique compound (called Ginkgolide), which improves blood flow to the brain.
Japanese Persimmon (Kaki) Leaves
Kaki persimmon leaves are rich in natural antihistamines and boast significantly higher vitamin C content than other sources, such as lemons. It helps reduce melanin levels, even skin tone, lightening dark spots, and enhancing skin collagen production. Additionally, they offer relief from itchiness and inflammation, reduce fluid retention (edema), and bolster immunity against flu and colds.
Japanese Mulberry (Kuwa) Leaves
With its light herbal flavor and subtle sweetness, Japanese Mulberry Leaves make a unique traditional Japanese drink beneficial for weight management. They are the only known source of DNJ (1-Deoxynojirimycin), known to combat diet-induced obesity. Drinking it can help reduce appetite and sugar cravings, decrease the absorption of carbohydrates, and lower blood sugar levels.
Japanese Arrowroot (Kuzu or Kudzu) Powder
Japanese Arrowroot, or Kuzu or Kudzu, comes in a silky, super-fine powder derived from its roots, rich in potassium, calcium, vitamin A, and antioxidants. Traditional Japanese Arrowroot Tea, often served hot as a dessert drink, is commonly used as a remedy for ailments like colds, sore throats, and upset stomachs. Additionally, it's an excellent alternative to starch and cornmeal, ideal for coating foods or thickening dishes, offering a smooth texture and glossy finish without any starchy taste, and dissolves quickly without clumping.
Japanese Ganoderma Mushroom (Saru•No•Koshikaké)
The Japanese Ganoderma Mushroom, known as Saru•No•Koshikaké, is celebrated for its myriad health benefits. Rich in beta-glucans, it activates the body's defenses against harmful pathogens, and antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-tumor properties. It makes a tea with a smooth taste and a hint of sweetness, complemented by its distinct mushroom flavor.
Japanese Perilla (Red Shiso or Akajiso)
Japanese Perilla, also known as Red Shiso or Akajiso, has a unique taste that blends basil and mint, enhanced by zesty and spicy notes. These leaves, belonging to the mint family, are integral to Japanese cuisine, serving as both a condiment and coloring agent. Nutritionally, Red shiso leaves surpass carrots in beta-carotene content and are abundant in vitamin A, iron, potassium, and antioxidant polyphenols like Anthocyanin and Rosmarinic acid. In traditional Japanese and Chinese medicine, they are used for their therapeutic properties, including stress reduction, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antiallergic benefits.
Copy and Quote Policy
The content you see on our pages, including images, graphics, and text is our exclusive copyrighted property. If you would like to post an excerpt from our website, you may do so on the conditions that you comply with the copyright policy in our Terms of Use, and on your post make a clear attribution to WAWAZA within close proximity of the excerpt, including a clickable link back to this page.













